REVERSED CHARGE MECHANISM (RC) - HOW IT WORKS (AS A CUSTOMER)
Understanding the Reverse Charge Mechanism as a customer
The reverse charge is covered by article 11E. Below we present a summary and some examples regarding the vat treatment of the RC and when there is a extra obligation for a Cyprus company or person (as a customer) to pay extra vat for a purchase he/she made as part of its business or not.
In a business transaction, there are 2 parties (1) the supplier and (2) the customer. Supplier is the entity or person that issues the invoice and customer is the person that accept the invoice.
According to the reverse charge mechanism, the supplier will not charge vat on the invoice and at the same time customer you will calculate vat (note 1) on a self-assessment basis (note 1). In an ideal scenario the entity/person the vat obligation will not be affected and there will be no obligation to pay any amount to the vat authorities. In practice you need make you self-assessment whether there is an obligation to pay any amount to the vat authorities.
Notes:
1. Calculation means to calculate the Vat Input (vat on purchases) and Vat Output (vat on sales) on the applicable vat rates of Cyprus (19%) and assess whether the Company can claim the Vat Input
See below 3 scenarios (A) Best Case Scenario (B) Worst Case Scenario (C) Middle Case Scenario

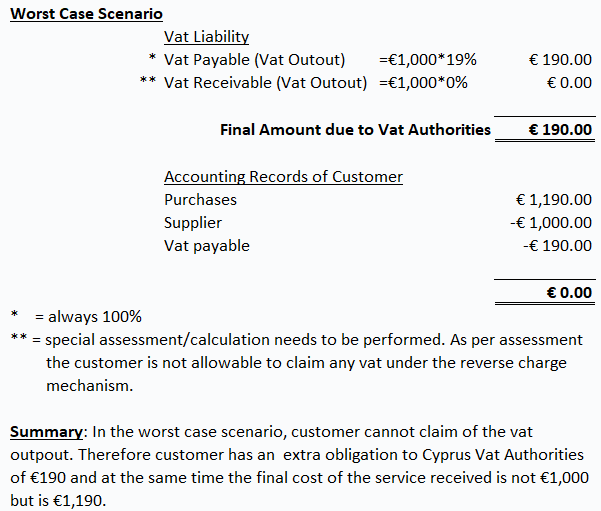
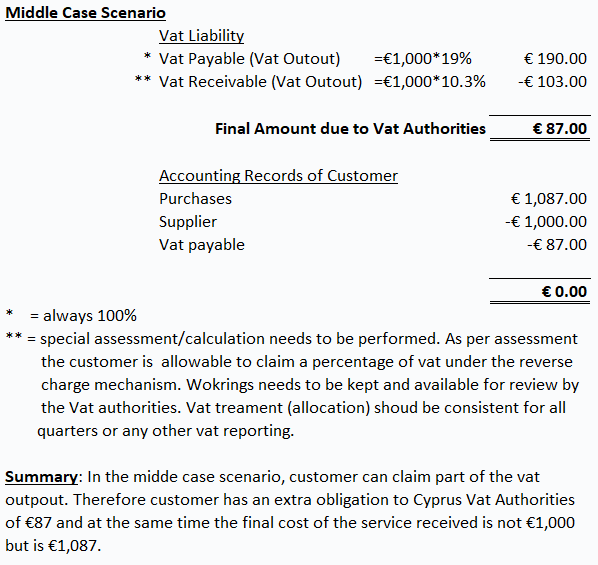
Reverse charge covers of a lot areas of the Vat regulations. Refer to article “Vat Reverse Charge – Comprehensive Guidance” by clicking here for a better understanding the following:
- To understand whether a transaction is falling under reverse charge
- When a transaction is exempted from reverse charge
- When you have the right to deduct the Vat Input
- What information needs the supplier to charge with 0% vat (on the invoice)
- If you are the supplier (issues invoices) when you can apply the reverse charge. What information you need?
